To check if your RAM is installed correctly, physically inspect the RAM sticks, verify recognition in BIOS/UEFI or Task Manager, and run a memory diagnostic tool.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to check if your RAM is installed correctly and troubleshoot any potential issues.
Understanding the Importance of Proper RAM Installation:
RAM (Random Access Memory) plays a vital role in your computer’s ability to run programs and manage tasks efficiently. If your RAM isn’t installed correctly, your system might not perform optimally, or worse, it might not boot up at all.
Proper installation ensures that your system can take full advantage of the memory capacity, providing you with a smoother computing experience.
Physical Inspection of RAM Installation:
The first step to check if your RAM is installed correctly is a physical inspection. Here’s how:
- Turn off your computer and disconnect it from the power source.
- Open your computer’s case or access the RAM compartment (for laptops, this might be a dedicated panel on the bottom).
- Check the RAM sticks: Ensure that each RAM stick is fully seated in its slot. The clips on either side of the RAM slots should snap into place when the RAM is properly installed. If the clips aren’t fully engaged, push down gently on the RAM sticks until they click into place.
- Check for dust or debris: Dust or debris in the slots can prevent proper contact. If necessary, use compressed air to clean the RAM slots and sticks.
Booting Up Your System:
Once you’ve verified that the RAM is physically installed correctly, it’s time to boot up your computer:
- Reconnect the power and turn on your computer.
- Listen for beeps: If your computer beeps repeatedly upon startup, it’s often a sign that the RAM isn’t installed correctly or isn’t compatible. Refer to your motherboard’s manual to interpret the beep codes.
Checking RAM in the BIOS/UEFI:
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is the first software that runs when you start your computer. It’s a great place to check if your RAM is recognized by your system:
- Access the BIOS/UEFI: To enter the BIOS/UEFI, you typically press a key (such as F2, F10, Del, or Esc) during startup. The exact key depends on your computer’s manufacturer, so refer to your manual or look for a message during boot.
- Locate the Memory Information section: In the BIOS/UEFI, find the section that displays memory or RAM information. This section should list the total amount of RAM installed and the number of slots being used.
- Verify the details: Compare the information shown with the actual amount of RAM installed. If the BIOS/UEFI shows the correct amount of RAM and identifies all installed sticks, then your RAM is installed correctly.
Also Read: How To Get More Ram Cyberpunk – Boosting Your Gaming Performance!
Using System Information Tools in Windows:
Windows provides built-in tools to check if your RAM is recognized and functioning properly:
System Information:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type msinfo32 and press Enter.
- In the System Information window, look for the “Installed Physical Memory (RAM)” entry. This should match the total amount of RAM you’ve installed.
Task Manager:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Go to the “Performance” tab and select “Memory” from the left-hand side.
- Here, you can see the total memory, the number of slots used, and the memory speed.
Running a Memory Diagnostic Tool:
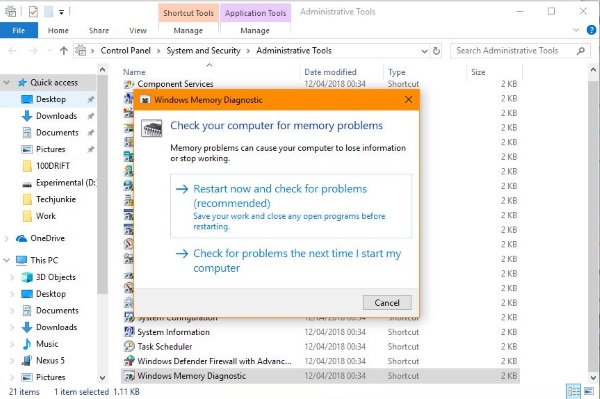
If you want to ensure that your RAM is functioning correctly without any errors, you can run a memory diagnostic:
Windows Memory Diagnostic:
- Press Windows + R, type mdsched.exe, and press Enter.
- Choose whether to restart your computer immediately and run the test, or schedule it for the next reboot.
- The tool will check your RAM for errors and report any issues.
- Third-Party Tools: Tools like MemTest86 can provide a more in-depth analysis of your RAM’s health. You can download this tool, create a bootable USB, and run it to check for errors.
Troubleshooting Common RAM Issues:
If your RAM isn’t recognized or your system isn’t running smoothly after installation, try these troubleshooting tips:
- Re-seat the RAM: Remove the RAM sticks and reinsert them, ensuring they are firmly in place.
- Test RAM sticks individually: If you have multiple RAM sticks, try testing each one individually by installing one stick at a time and booting your computer. This can help identify if a specific stick is faulty.
- Check compatibility: Ensure that your RAM is compatible with your motherboard and that you haven’t exceeded the maximum RAM capacity.
- Update your BIOS/UEFI: Sometimes, a BIOS/UEFI update is needed to properly recognize new RAM.
FAQ’s
1. How do I know if my RAM is installed correctly?
Check for physical seating, verify in BIOS/UEFI, and use system information tools to confirm the RAM is recognized.
2. What happens if my RAM isn’t installed correctly?
Your computer may not boot, may beep on startup, or might not recognize the full amount of RAM.
3. Can I install RAM myself?
Yes, installing RAM is relatively straightforward and can be done with basic tools and careful handling.
4. How do I access the BIOS/UEFI to check my RAM?
Press the appropriate key (often F2, F10, Del, or Esc) during startup to enter the BIOS/UEFI.
5. What should I do if my computer doesn’t recognize my new RAM?
Re-seat the RAM, check compatibility, and ensure the RAM slots are clean and free of debris.
6. How much RAM does my computer need?
It depends on your usage. For basic tasks, 8GB is usually sufficient, while gaming and professional tasks might require 16GB or more.
7. Can faulty RAM be repaired?
Faulty RAM usually cannot be repaired and should be replaced if it fails diagnostic tests.
8. Does the order of RAM sticks matter?
Yes, some motherboards require RAM to be installed in specific slots or configurations for optimal performance.
9. What tools can I use to check if my RAM is functioning correctly?
Use Windows Memory Diagnostic, MemTest86, or other third-party tools to test RAM health.
10. Can updating my BIOS/UEFI help with RAM issues?
Yes, sometimes a BIOS/UEFI update can improve RAM compatibility and stability.
Conclusion
Checking that your RAM is installed correctly is a vital step to ensuring your computer runs efficiently. By following these steps—physically inspecting the RAM, checking in the BIOS/UEFI, using system tools, and running diagnostics—you can confirm that your RAM is properly installed and functioning. If you encounter any issues, the troubleshooting tips provided can help resolve common problems. Ensuring your RAM is correctly installed will optimize your system’s performance, leading to a smoother and more reliable computing experience.

































Leave a Reply